How to Become a Surgeon: Complete Guide to Your Medical Career
Learn about pursuing a career as a practicing surgeon.
A career in surgery is one of the most challenging yet rewarding paths in medicine.
Surgeons have the privilege of making life-changing impacts through their expertise, precision and compassion, combining advanced knowledge of the human body with hands-on skill.
If you’re wondering how to become a surgeon, this guide will outline the steps, from your first college course to your first day in the operating room.
What Is a Surgeon?
A surgeon is a highly trained medical professional who performs operations to treat injuries, diseases and deformities. These procedures can range from life-saving interventions to elective surgeries that improve patients’ quality of life. There are several different types of surgeon, with specializations ranging from general surgery to orthopedics to cardiothoracic surgery.
Surgeons are not only skilled in technical procedures but also adept at patient care, decision-making and collaborating with multidisciplinary teams. This rewarding profession demands a high level of commitment, but the impact you’ll make on patients’ lives often makes it all worthwhile.
What Skills Do Surgeons Have?
To excel in surgery, professionals must possess a blend of technical expertise and interpersonal abilities. Below are some essential skills needed to be a surgeon:
- Manual dexterity and precision: Steady hands and exceptional motor skills are critical during intricate procedures.
- Problem-solving abilities: Surgeons must assess complex cases and make quick, informed decisions.
- Communication skills: Effective communication with patients, families and medical teams is essential.
- Leadership and teamwork: Leading surgical teams requires collaboration and clear directives.
- In-depth knowledge: A surgeon’s understanding of human anatomy, diseases and treatment strategies must be exceptional.
- Emotional resilience: Managing high-pressure situations and coping with potentially upsetting outcomes are part of the job.
- Physical stamina: Long hours in the operating room require sustained focus and energy.
These surgeon skills are honed throughout years of education and practice, ensuring the highest standard of care for patients.
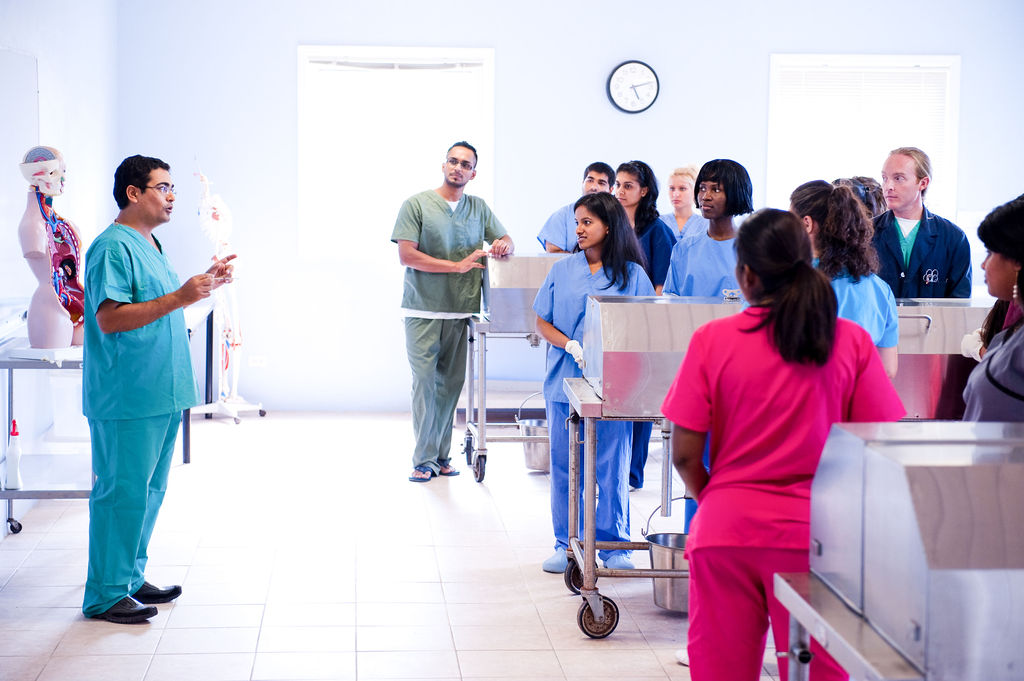


Why Choose a Career in Surgery?
Pursuing a career as a surgeon offers profound personal and professional fulfillment. Surgeons play a pivotal role in the healthcare system, restoring health and often saving lives.
The profession challenges individuals to continually learn, master advanced techniques and contribute to medical innovation. It is also dynamic, with constant advancements in technology, such as robotic surgery and minimally invasive techniques, which make it an ever-evolving field.
Additionally, surgery is not just about technical skill but also about earning the trust of patients and their families, as you guide them through some of the most critical moments of their lives. This can be incredibly fulfilling, both personally and professionally.
Finally, the general surgeon starting salary is one of the highest in medicine, reflecting the dedication and expertise required. This financial incentive is understandably very appealing for aspiring physicians.
How to Become a Surgeon
The journey for aspiring surgeons is long but structured. Here’s an overview of the steps to becoming a surgeon:
1. Earn Your Bachelor’s Degree
Your journey to becoming a surgeon begins with completing an undergraduate degree, typically in a science-related field like biology, chemistry or physics. While a pre-med track is not mandatory, it’s highly recommended because it provides the prerequisites required for medical school. Courses such as organic chemistry, physics and anatomy are foundational for your success.
Beyond academics, gaining experience through internships, volunteering at hospitals or shadowing physicians can strengthen your application to medical school. This is also a good time to prepare for the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT), which evaluates the readiness of U.S. students for advanced medical studies.
2. Complete Medical School
A medical school 4-year MD program is where you build the core knowledge and skills required to practice medicine. The first two years typically focus on classroom learning in subjects like anatomy, pharmacology and pathology. The final two years are dedicated to clinical rotations, where you gain hands-on experience in various specialties, including surgery. Clinical rotations are an exciting opportunity to gain real insights into the world of a surgeon, while considering where you may like to pursue a surgical residency.
Hear from an MUA graduate who is currently in a surgery residency:
Throughout your time at medical school, maintaining a strong academic record and building relationships with mentors can set you up for success in securing a competitive residency placement after graduation.
3. Undergo Residency
The first step in an aspiring surgeon’s journey after medical school is residency. Post-graduation, aspiring surgeons enter a residency program, which typically lasts 5–7 years, depending on the specialty. General surgery residencies offer comprehensive training in surgical techniques, patient management and operating room protocols.
Residency is intensive, blending hands-on practice in surgical rooms, outpatient clinics and emergency settings with mentorship from experienced surgeons.
4. Obtain a License
To practice as a surgeon, you must pass a licensing examination, such as the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 3. This rigorous test assesses your medical knowledge, clinical skills and ability to provide safe and effective patient care.
Passing this exam demonstrates your readiness to take on the responsibilities of a practicing physician.
5. Earn Certifications
While licensing allows you to practice, obtaining board certification in your chosen specialty enhances your credibility and career prospects. Certification typically involves passing an additional examination administered by a professional board, such as the American Board of Surgery.
Board certification signals a commitment to excellence and is often required by employers.
6. Complete a Fellowship
If you want to specialize further to pursue a particular surgical discipline, completing a fellowship is the next step. Fellowships provide advanced training in areas like pediatric surgery, oncology surgery or cardiovascular surgery. These programs typically last 1–3 years and allow you to gain expertise in highly specialized procedures.
7. Prepare a CV or Resume
As you approach the end of your training, prepare a professional CV highlighting your education, training, certifications and clinical experience. Tailor your CV to the specific surgical roles or subspecialties you are pursuing and include any research or publications.
8. Explore Job Opportunities
Finally, explore job opportunities within hospitals, private practices or academic institutions. Networking through residency programs and attending surgical conferences can help you by connecting you with potential employers.
Conclusion
Becoming a surgeon requires perseverance, passion and an unwavering commitment to excellence.
If you’re ready to embark on this life-changing journey, consider the MD program at Medical University of the Americas. MUA’s curriculum is designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills to succeed in this challenging and rewarding career. If you’re ready to proceed, apply today or contact us for more information.
FAQs About Surgeons
It typically takes 12–15 years to become a surgeon. This includes four years of undergraduate education, four years of medical school and 4–7 years of residency training. If you choose to pursue a fellowship for a subspecialty, it may add another 1–3 years to your timeline. This long path ensures you gain the knowledge, skills and experience necessary for this demanding profession.
Yes, surgeons are doctors. They complete medical school and additional specialized training to perform surgical procedures. If you’re wondering “what is the role of a surgeon?”, then it is this key ability to perform surgeries that marks them out from other doctors. While all surgeons are doctors, not all doctors are surgeons, as some pursue non-surgical specialties.
A career in surgery is an excellent choice for those passionate about medicine, problem-solving and patient care. It offers immense personal and professional rewards, including the opportunity to save lives and make a significant impact in your community. Financially, it’s one of the highest-paying medical fields, reflecting the dedication and expertise required.
Yes, surgeons are physicians who specialize in operative procedures. Like other physicians, they complete medical school and are licensed to practice medicine. However, their additional training focuses on diagnosing conditions that require surgical intervention and performing those surgeries.

Useful links
Get in touch for more information