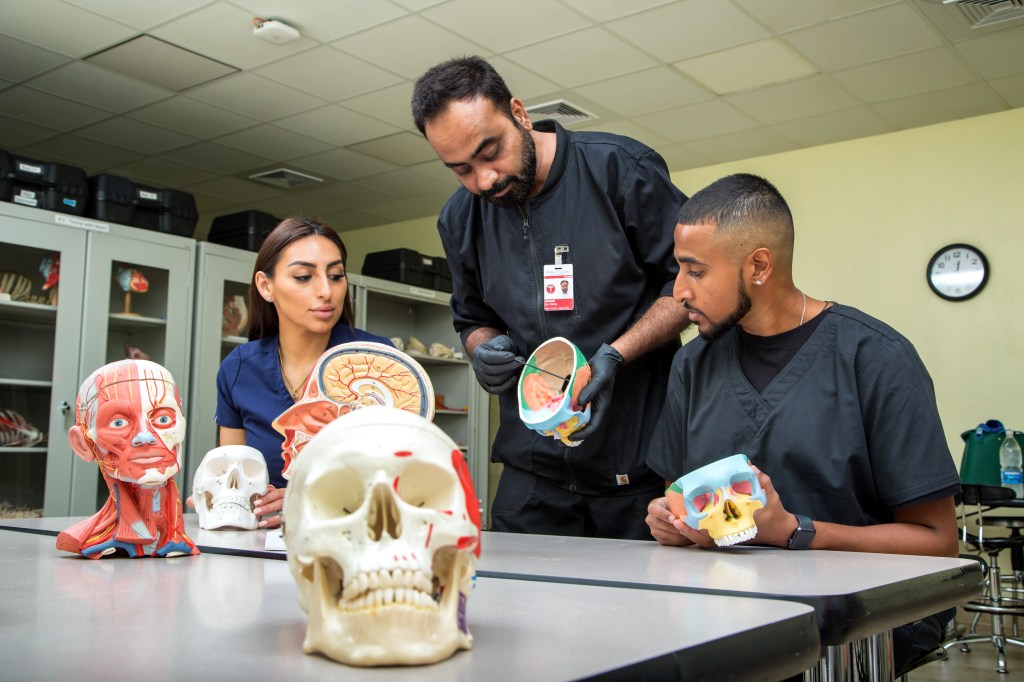
What Are the Different Types of Doctors and What Do They Do?
Doctors are essential to the field of healthcare, providing invaluable services that keep individuals and communities healthy. With a wide variety of medical fields to choose from, doctors can specialize in different areas to cater to the diverse health needs of patients. Understanding the different types of doctors and what they do is important, especially if you’re planning to pursue a career in medicine. This blog will explore the roles of various medical doctors, breaking them down into three main categories: primary care physicians, specialists and surgeons.
Whether you’re interested in becoming a doctor yourself or want to understand the healthcare system better, learning about these different types of physicians will give you a clearer picture of what different kinds of doctors do.
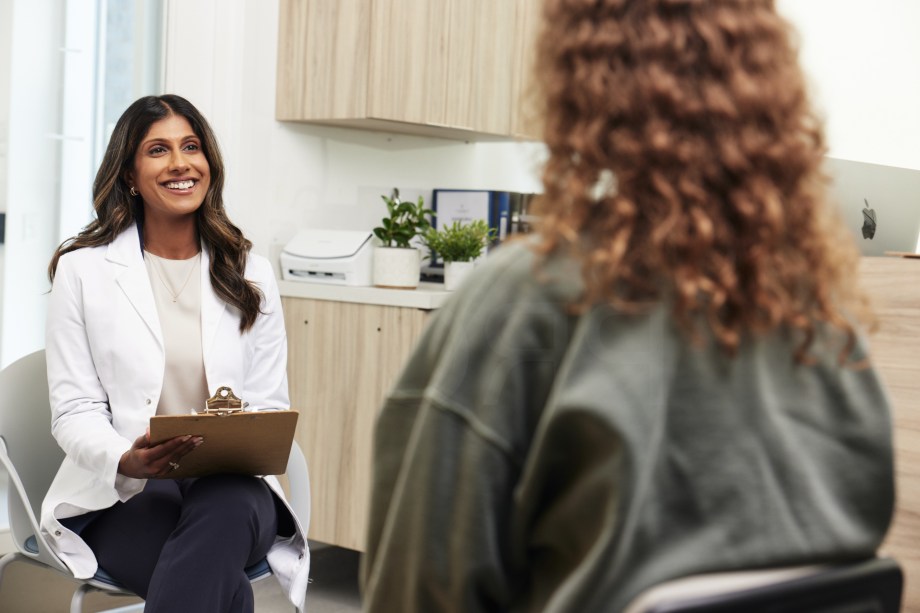

Primary Care Physicians
Primary care physicians (PCPs) serve as the first point of contact for patients seeking medical support. They provide comprehensive care, focusing on prevention, diagnosis and treatment of common conditions. These doctors are essential for coordinating patient care and can refer patients to specialists if needed.
Family Medicine Doctors
Family medicine doctors, also known as general practitioners, are among the most versatile of all primary care physicians. They are trained to provide care for patients of all ages, from newborns to the elderly. These physicians diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions, from acute illnesses like infections and injuries to chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. They also perform routine check-ups, vaccinations and health screenings. Family doctors often form long-term relationships with their patients, offering personalized, comprehensive care over a lifetime.
Pediatricians
Pediatricians specialize in the health and medical care of infants, children and adolescents. Their role extends beyond treating illnesses; they also monitor a child’s growth, development and behavioral health. Pediatricians are instrumental in early diagnosis of developmental delays, congenital conditions and childhood diseases.
Given their focus on younger patients, pediatricians also guide parents through important health decisions like immunizations, nutrition and mental health. They often work closely with specialists to manage complex childhood conditions and ensure holistic care.
Internists
Internists, or doctors of internal medicine, focus on adult health. These physicians treat a wide range of conditions, from common ailments like infections to more complex diseases like diabetes and heart disease. While family doctors treat patients of all ages, internists typically concentrate on adults, making them experts in adult chronic disease management. Many internists go on to specialize in specific areas of internal medicine, such as cardiology or gastroenterology.
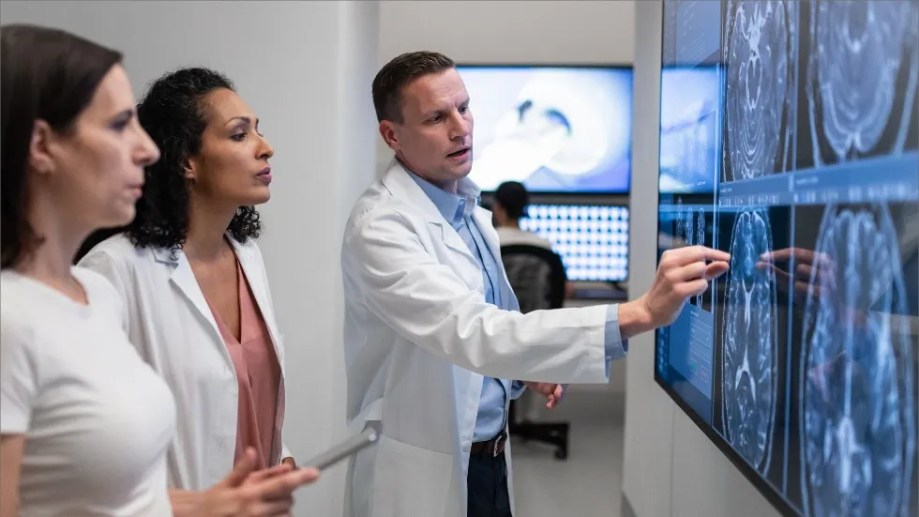

Specialists
While primary care physicians manage general health concerns, specialist doctors focus on specific systems, organs or medical conditions. These types of doctors have additional training and expertise in a particular field, allowing them to diagnose and treat more complex or specialized conditions.
Cardiologists
Cardiologists specialize in heart and cardiovascular health. They diagnose and treat conditions like heart disease, hypertension, arrhythmias and heart failure, and perform procedures like stress tests, echocardiograms and angioplasty. Cardiologists play a key role in managing chronic heart conditions, helping patients improve their quality of life through medications, lifestyle changes and advanced procedures.
Dermatologists
Dermatologists specialize in skin, hair and nail conditions. From treating acne and eczema to diagnosing skin cancer, dermatologists handle a wide range of issues. They also perform cosmetic procedures, such as laser treatments and Botox injections. Because skin health can reflect overall wellness, dermatologists often collaborate with other doctors to address underlying health problems.
Neurologists
Neurologists focus on the brain, spinal cord and nervous system. They diagnose and treat conditions such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, migraines and strokes. Neurologists use diagnostic tools such as MRI scans and electroencephalograms (EEGs) to detect and treat neurological conditions.
Ophthalmologists
Ophthalmologists are medical doctors who specialize in eye and vision care. Unlike optometrists, ophthalmologists can perform surgeries, including cataract removal and corrective laser surgery. They manage conditions like glaucoma, macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy, helping preserve and improve patients’ vision.
Obstetricians and Gynecologists (OB/GYNs)
OB/GYNs specialize in women’s reproductive health, from adolescence through menopause and beyond. Obstetricians focus on pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum care, while gynecologists manage broader women’s health issues, including menstrual disorders, hormonal imbalances and reproductive health. Many OB/GYNs combine both roles, offering comprehensive care for women.
Endocrinologists
Endocrinologists specialize in the endocrine system, which includes glands that regulate hormones. They treat conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, metabolic issues and osteoporosis. Endocrinologists often manage chronic conditions that require long-term monitoring and hormone therapies.
Gastroenterologists
Gastroenterologists diagnose and treat diseases related to the digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, intestines and colon. Common conditions treated by gastroenterologists include irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and liver diseases like hepatitis. Gastroenterologists perform endoscopic procedures like colonoscopies to examine and treat digestive tract issues.
Nephrologists
Nephrologists are specialists in kidney health. They diagnose and treat kidney diseases, manage dialysis for patients with kidney failure and monitor patients with conditions like hypertension that affect kidney function.
Pulmonologists
Pulmonologists focus on lung and respiratory conditions. They diagnose and treat illnesses like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and pneumonia. Pulmonologists are crucial in managing patients with long-term respiratory conditions and often collaborate with critical care specialists in treating severe cases.
Otolaryngologists
Also known as ear, nose and throat (ENT) doctors, otolaryngologists treat a range of conditions affecting these areas. From chronic sinus infections and tonsillitis to hearing loss and balance disorders, they diagnose and perform surgeries to improve patients’ quality of life.
Psychiatrists
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in mental health, including the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mental illnesses. They can prescribe medications and provide therapy for conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Unlike psychologists, psychiatrists are licensed to prescribe medications.
Oncologists
Oncologists specialize in diagnosing and treating cancer. They often work in multidisciplinary teams, coordinating care with surgeons, radiologists and other specialists to manage a patient’s cancer journey from diagnosis through treatment and into remission or palliative care. There are different types of oncologists, such as medical, surgical and radiation oncologists, each focusing on a specific aspect of cancer treatment.
Radiologists
Radiologists use imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRIs and CT scans to diagnose and monitor diseases. Their role is crucial in providing accurate imaging reports to guide other physicians and surgeons in treatment plans. Some radiologists specialize in interventional radiology, performing minimally invasive procedures using imaging technology.
Rheumatologists
Rheumatologists treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and gout. These conditions often involve chronic pain and joint damage, and rheumatologists work to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Anesthesiologists
Anesthesiologists are responsible for managing pain and sedation during surgeries. They administer anesthesia and monitor patients during surgical procedures to ensure safety and comfort. Beyond surgery, anesthesiologists also manage chronic pain conditions and provide critical care in emergency situations.
Geriatricians
Geriatricians specialize in the care of older adults, managing age-related conditions such as dementia, osteoporosis and frailty. They focus on improving the quality of life and providing compassionate, patient-centered care for elderly patients.
Surgeons
Surgeons perform operations to treat diseases, injuries and deformities. Their roles demand high levels of precision and skill, as they are responsible for both life-saving surgeries and elective procedures that improve quality of life. There are several different types of surgeons covering a range of different surgical disciplines.
Orthopedic Surgeons
Orthopedic surgeons focus on the musculoskeletal system, performing surgeries to repair broken bones, replace joints and treat conditions such as arthritis and sports injuries. They are often involved in complex reconstructions and joint replacements.
Cardiac Surgeons
Cardiac surgeons focus on surgeries of the heart and surrounding vessels. Common procedures include coronary artery bypass grafting, valve repair and heart transplants. Cardiac surgeons often work in emergency settings, performing life-saving operations on patients with heart disease.
Neurosurgeons
Neurosurgeons specialize in surgical procedures involving the brain, spinal cord and nervous system. They perform intricate surgeries to treat conditions such as brain tumors, spinal cord injuries and chronic pain conditions. Neurosurgery is one of the most complex surgical specialties, requiring precision and skill to address critical neurological conditions.
Plastic Surgeons
Plastic surgeons perform both reconstructive and cosmetic procedures. Reconstructive surgery includes procedures such as repairing cleft palates and breast reconstruction after cancer surgery. Cosmetic surgery includes procedures like rhinoplasty and facelifts.
Check out this video about Medical University of the Americas (MUA) alum Sheldon Vogt, MD, who is undertaking a General Surgery residency at Loma Linda University Health in California:
At MUA, we’re proud to help our students pursue their medical career passions, whether as a primary care practitioner, specialist or surgeon!
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of doctors and what they do can help you navigate the healthcare system more effectively. Whether you’re visiting a primary care physician for routine care or seeing a specialist for a specific health concern, these doctors play vital roles in maintaining and restoring health.
If you’re committed to becoming a practicing physician and are inspired by one or more of the roles listed above, MUA can help you get there! Our 4-Year MD Program provides a rigorous and comprehensive education that will help equip you with the knowledge and skills to make a successful impact in healthcare.
If you’re interested or have any questions, please contact us.
FAQs About Different Kinds of Doctors
The difficulty level associated with becoming different kinds of doctors often depends on the specialty, with neurosurgeons, cardiac surgeons and other highly specialized fields requiring the longest training and most rigorous residency programs. These specialties involve complex procedures and high-risk situations, which necessitates undertaking many demanding years of education and hands-on experience. Neurosurgery, in particular, is known to be one of the most challenging due to the intricacies of brain and spinal cord surgeries.
Some of the most in-demand doctor specialties include primary care physicians, especially family medicine doctors and internists, as well as specialists in fields like cardiology, orthopedics, psychiatry, oncology and anesthesiology. These specialties address some of the most prevalent health concerns, such as heart disease, mental health, cancer and surgical needs, making them critical in today’s healthcare system.
A primary care physician (PCP) is a doctor who provides general healthcare services, including preventive care, health education and treatment for common illnesses. PCPs, such as family doctors, pediatricians and internists, are usually the first doctors patients see for non-emergency issues. Specialists, on the other hand, focus on a specific area of medicine, diagnosing and treating more complex or specific conditions. PCPs often refer patients to specialists for advanced care.
Orthopedic surgeons, cardiac surgeons and neurosurgeons are often among the highest-paid doctors due to the complexity and risk associated with their procedures. Other highly compensated specialties include anesthesiologists and plastic surgeons. Compensation can vary based on location, demand and experience.
Some of the rarest types of doctors include immunologists, who specialize in immune system disorders, and geneticists, who focus on hereditary diseases and conditions. Specialists in fields like pediatric surgeons for rare conditions or doctors who focus on very specific parts of the body can also be rare due to their highly specialized knowledge and limited demand.
Yes, it is possible for a doctor to be trained in and certified for multiple specialties. Some doctors pursue dual or even triple board certification, often in related fields. For example, a doctor might be certified in both internal medicine and cardiology, or in pediatrics, family medicine and emergency medicine. However, this requires additional years of training and examinations in each specialty.
