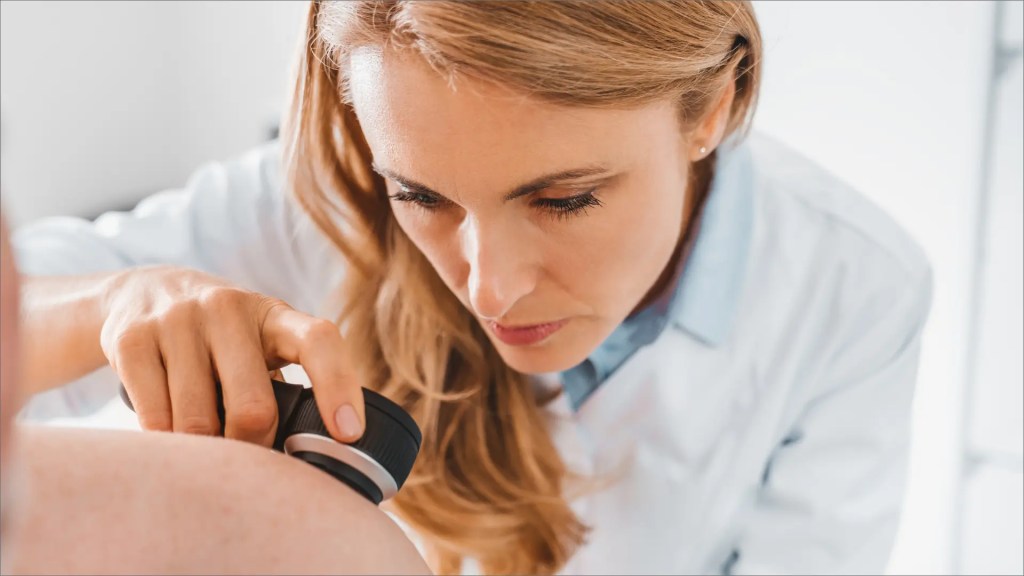
A Guide to Becoming a Dermatologist
Read our detailed guide about the education and training required to become a practicing dermatologist.
Last updated: November 5, 2024
Are you interested in helping people maintain healthy skin? If this sounds like you, then a career in dermatology might be the perfect choice. Working as a dermatologist, you will diagnose and treat skin conditions while also helping your patients to look and feel their best.
Read on to find out more about what a dermatologist does, how you can become one and whether a career in dermatology is right for you.

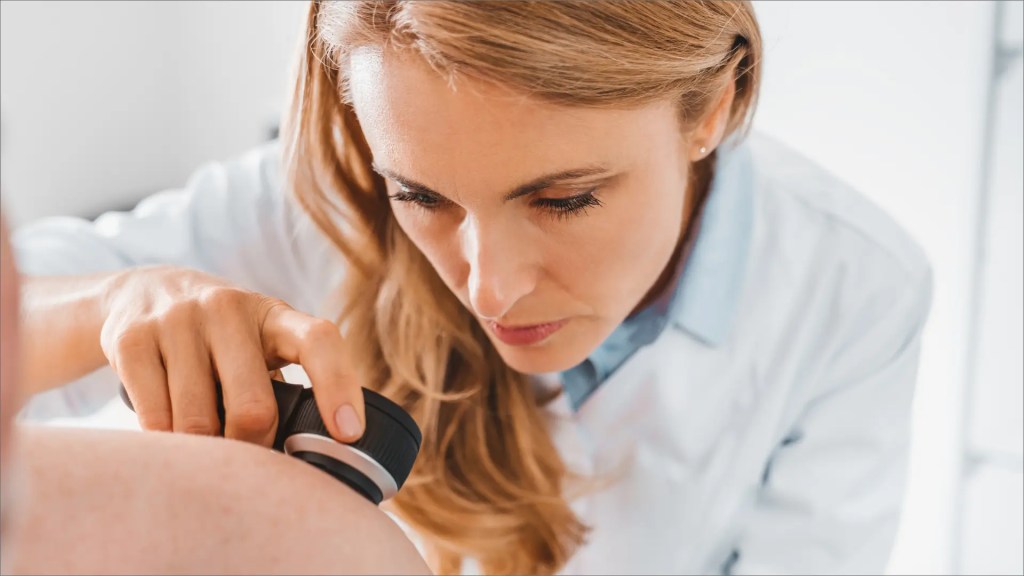
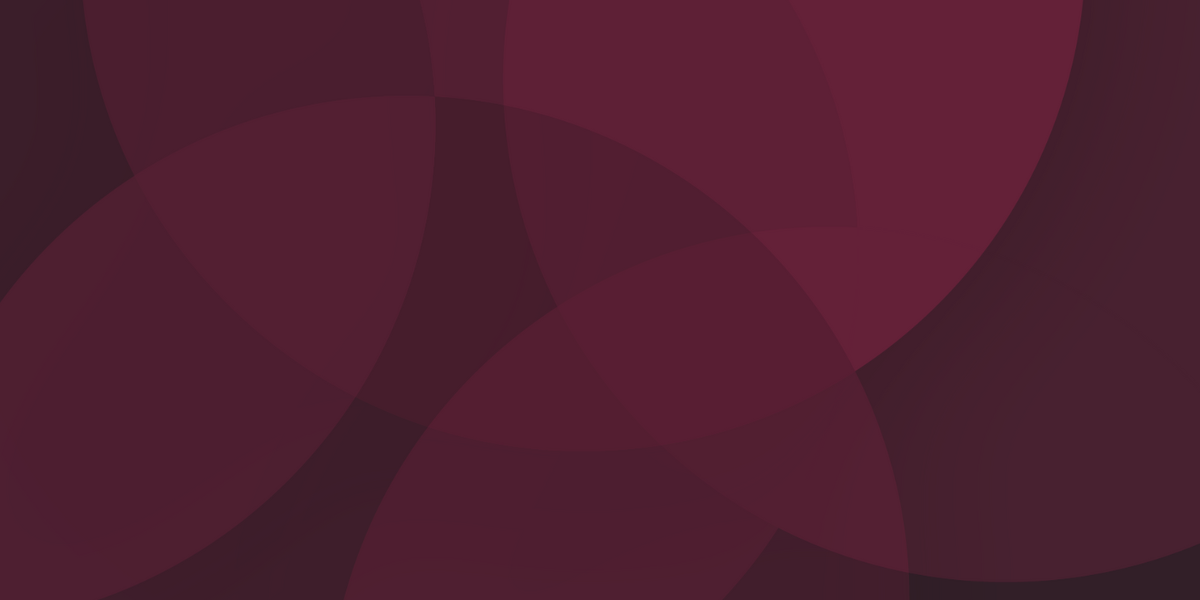
What is a dermatologist?
A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the prevention and treatment of more than 3,000 hair, skin, nail and mucous membrane conditions. Millions of people visit dermatologists each year in countries around the world. Dermatologists provide care to people of all ages, for such conditions as:
- Acne: Based on the severity of the acne, a dermatologist will treat it with topical applications, chemical peels, the removal of large cysts or light therapies (such as lasers).
- Dermatitis: Dermatitis includes skin conditions that cause irritation and inflammation, such as cradle cap, eczema and allergic reactions.
- Hair loss: A dermatologist will determine the underlying cause of hair loss and treat it if possible.
- Infections: A dermatologist can diagnose the cause of infections and prescribe an appropriate treatment.
- Nail problems: Common nail issues treated by dermatologists are spots, nail separation and discoloration.
- Skin cancer: A dermatologist can remove cancer cells and monitor the patient to ensure the cancer doesn’t return.
Internal medicine doctors and general practitioners can diagnose and treat many of these conditions as well. However, a dermatologist has a deeper understanding and greater experience with these issues. Primary care doctors will frequently refer patients to a dermatologist for specialized care.
Besides these cosmetic and medical skin-related issues, dermatologists can also recognize the symptoms of other serious underlying health issues. The skin is the body’s largest organ and the first line of defense against injury and pathogens. It can often be a good indicator of overall health. For instance, diabetes can impact the skin’s appearance and a dermatologist can be the first healthcare provider to recognize the signs.
What does a dermatologist do?
Like most medical doctors, the day-to-day duties of a dermatologist are as varied as the patients they care for. They provide life-changing diagnoses and treatments to restore health, prevent illness and improve life for both children and adults. Dermatologists also provide their patients with education and preventative care for skin and other related health issues. For example, they may perform skin surveys to find precancerous lesions among patients with a high risk of skin cancer. This can help to alleviate pain and vastly improve the lives of patients living with debilitating skin conditions. As part of their dermatologist job roles, doctors will:
- Meet with patients: A dermatologist will record the patient’s medical history, perform patient examinations, spot any irregularities and discuss a diagnosis.
- Develop treatment plans: Dermatologists may prescribe medications, remove the abnormality, perform surgery or take biopsies for further research.
- Address cosmetic concerns: A dermatologist uses tools such as lasers to treat birthmarks, Botox to tackle wrinkles and skin grafting for patients with severe scarring.
- Perform follow-up examinations or treatments: Dermatology treatments often need numerous sessions to resolve the issue and for the dermatologist to track patient progress.
What do dermatologists study?
Dermatologists study and train to carry out a variety of procedures, such as:
- Biopsies: Dermatologists perform different biopsy procedures to diagnose or rule out conditions such as skin cancer.
- Chemical peels: This treatment removes damaged skin, rejuvenates new skin and reduces the signs of aging.
- Cosmetic injections: Dermatologists use cosmetic injections such as fillers or Botox injections to help reduce the appearance of sagging skin and wrinkles
- Cryotherapy: A treatment for certain skin conditions such as tumors, warts and skin tags.
- Dermabrasion: A dermatologist uses this exfoliating procedure to reduce the appearance of age spots, fine lines, precancerous skin patches and acne scars.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy can be used to remove moles, warts, tattoos, sun spots, blemishes, acne scars, unwanted hair or wrinkles.
- Mohs surgery: Dermatologists use this type of skin cancer surgery to remove thin layers of tissue around a tumor while looking for signs of other cancer cells.
- Sclerotherapy: Dermatologists use sclerotherapy to treat varicose veins by injecting chemicals into damaged veins.
- Surgical excision: A dermatologist performs a surgical excision to remove growths like lesions, moles and skin tags.
- Tumescent liposuction: The removal of unwanted fat from certain areas of the patient’s body.
How to become a dermatologist?
To become a dermatologist in the United States, you will need to have an up-to-date license. While requirements will slightly vary depending on the state, most require dermatologists to hold a degree from an accredited medical school, undertake a residency program and pass the U.S. Medical Licensing Exams (USMLE). Therefore, to become a dermatologist, you will need to:
- Attend medical school
- Pass the first two parts of the USMLE
- Complete your residency
- Pass the third part of the USMLE
- Get a license
- Become board certified
How long does it take to become a dermatologist?
It can take 11-12 years to become a dermatologist, depending on your level of specialization post-residency. This includes time spent as an undergraduate (4 years), in medical school (4 years) and completing residency (3 years). This journey can be accelerated by taking certain medical education pathways, such as MUA’s 6-Year BSc/MD Program, where students enter medical school directly out of high school and bypass the four years of undergraduate studies.
Residencies and fellowships for dermatologists
After completing medical school, dermatologists will typically spend the next three years in an ACGME-accredited dermatology school residency training program. There are 150 accredited dermatology programs in the United States and nine programs in Canada. Approximately 530 residents graduate every year.
Following dermatology certification by the American Board of Dermatology (ABD), a dermatologist can choose to pursue further dermatology schooling via specialized training in dermatopathology, micrographic surgery, pediatric dermatology and dermatologic oncology. This often involves one year of training in an approved fellowship training program.
How much do dermatologists make?
The average dermatologist salary in the United States is $100,000 per year, equivalent to $48 per hour. Entry-level dermatology positions typically start at around $41,000 a year, while more experienced dermatologists can make up to $350,000 a year.
Salary ranges vary considerably depending on your education, certifications and years of experience. Your geographical location can also impact how much you will make as a dermatologist. The table below shows the average salaries of dermatologists across some U.S. regions:
| Region | Annual Salary per Year |
|---|---|
| Florida | $100,000 |
| California | $59,080 |
| New York | $156,000 |
| Massachusetts | $177,500 |
| Pennsylvania | $100,000 |
| Washington | $40,000 |
| South Dakota | $500,000 |
| Ohio | $100,000 |
| Indiana | $100,000 |
Is dermatology right for you?
To build a successful dermatologist career, you need to take a thorough and disciplined approach to your work and have strong observational skills. You also need a strong interest in medical science and research, as new technologies are constantly transforming how dermatologists assess, diagnose and treat.
But dermatology isn’t all about hard work. It is one of the key medical and healthcare specialties that provide a high standard of job satisfaction and work-life balance. There are several reasons that people choose to become dermatology doctors, including:
- Standard full-time working hours of 9am to 5pm
- Access to a wide variety of clinical cases
- Opportunity to work remotely
- Great work/life balance
- High rates of job satisfaction
However, as with most professions, dermatology also has its challenges:
- A large amount of telephone-based appointments
- Outpatient-based specialty
- Highly competitive field
- Big jump in clinical responsibility from medical training
What skills do you need to be a dermatologist?
You should consider pursuing a career in dermatology if you have the following dermatologist requirements:
- Attention to detail: Dermatologists need to have excellent attention to detail to identify and track minor changes in a patient’s skin condition.
- Communication skills: Dermatologists must communicate diagnoses and treatment information to patients. They must speak and write clearly and be able to listen carefully.
- Organization skills: Working with hundreds of patients every month requires a dermatologist to have excellent organizational and record-keeping skills.
- Problem-solving skills: Dermatologists need strong problem-solving skills to identify effective treatments when assessing skin conditions.
- Excellent memory: Dermatologists must have a strong memory to recall the thousands of health problems that can manifest on hair, nails and the skin, and to recognize the symptoms of these conditions.
- Enjoy making people look good: The cosmetic side of dermatology requires a dermatologist to feel good about making their patients look good.
Medical University of the Americas (MUA)
If you’re interested in becoming a dermatologist, we would love to help you get there!
We offer an expansive medical education, hands-on training, individualized support and a variety of student services to ensure that our aspiring physicians receive the personal and learning opportunities they need to succeed in medicine. We also offer an MD program that grants graduates a Doctor of Medicine, which is an important dermatologist degree.
Or consider one of our pre-med programs, which help those without a typical pre-medical undergraduate degree prepare for the MD program. Wherever you are in your medical career journey, we can help you get on the right path to success as a dermatologist!
To learn more about MUA and the island of Nevis, check out this video from Premier Mark Brantley:
If you have any questions or need any admissions-related support, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
FAQs About Dermatology
While a Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) is a useful degree for those pursuing a career as a dermatologist, it is not required. In fact, you will likely still need to achieve a Doctor of Medicine or other higher-level degree. At MUA, those with an MBBS degree may be eligible to enter our MD program with advanced standing, which will help you progress more quickly along your pathway to a career in medicine. Learn more here.
Dermatology is a competitive medical field due to all of the positive benefits associated with being a dermatologist, such as work/life balance, job satisfaction and workplace flexibility. As with all medical disciplines, it is important to choose a medical school with a proven track record of success helping students secure post-graduate residencies.
The most “standard” dermatologist career pathway is to successfully complete a four-year undergraduate degree in a pre-medical field of study, an MD program at an accredited medical school and a 3-year dermatology residency program. MUA is proud to support students pursuing this pathway, as well as students who lack the usual or any undergraduate degree and who are pursuing alternative pre-medical pathways to a career in dermatology.
Yes, licensed dermatologists can perform surgeries such Mohs surgery and surgical excisions.
